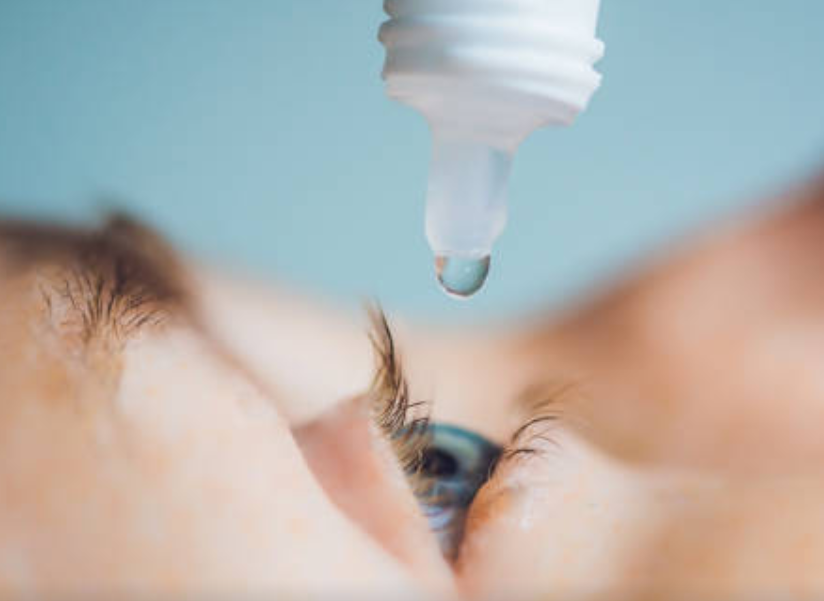
Polyvinyl Alcohol Material
- Medical Use PVA
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a synthetic, biocompatible and toxicologically safe polymer that is exceptionally well suited for a variety of pharmaceutical applications: In tablet coatings, for example, it protects the tablet from environmental humidity, in eye drops it moistens the eye, and in cell fermentation processes Polyvinyl Alcohol prevents bubble rupture to protect cells from shearing. Merck makes it easy to fully exploit the possibilities of Polyvinyl Alcohol
——SSC
- An Overview Of PVA Material
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is a vinyl polymer joined by only carbon–carbon linkages. The linkage is the same as those of typical plastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, and of water-soluble polymers such as polyacrylamide and polyacrylic acid.
——Sciencedirect.com
- Review of the oral toxicity of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)
Keywords: Polyvinyl alcohol; Poly(vinyl alcohol); Partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol; PVA; Film coating polymer; Excipient; Vinyl alcohol polymer; Ethenol homopolymer
——C.C. DeMerlis*, D.R. Schoneker
PVA Fabric
- Vinylon is a classic application of PVA in textile field
PVA is hydrophillic so the textile made from this material keeps this properties. Though its clothing property may be far less popular than other synthetic fibers, Vinylon is still known for its properties of moisture absorption and wear resistance and can substitute some cotton-made bedding, knitwear, decorative cloth, canvas, uniform, work clothes, fishing net and curtain.
——Sibikon R&D
- Polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber based three phase wound dressings for sustained wound healing applications
Herein we present our research on a novel three phase antibacterial wound dressing prepared from car- bon nanotubes, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers. The AgNPs were generated on carbon nanotubes surfaces to synthesize carbon nanotubes-AgNP nanoparticles which were added into the polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers prior to electrospinning to prepare PVA/carbon nanotubes-AgNP composite nanofibers. All characterizations confirmed the three phase nanofiber architecture.
——
- Study on Evaluation Method for PVA Fiber Distribution in Engineered Cementitious Composite
The distribution of fibers in Engineered Cementitious Composite (ECC) is one of the most important factors in terms of the mechanical performance of the composite. However, estimation of fiber distribution in ECC has been a difficult problem because of the lower contrast of organic fiber in the cement material.
——
PVA film
- PVA as A Viable Membrane
In this work, we report separator membranes from crosslinking of two polymers, such as poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) with an ionic polymer poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic anhydride) (PMVE-MA). Such interpolymer-networked systems were extensively used for biomedical and desalination applications but they were not examined for their potential use as membranes or separators for batteries.
——ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Separator Membrane from Crosslinked PVA and Other Polymer
In this work, we report separator membranes from crosslinking of two polymers, such as poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) with an ionic polymer poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic anhydride) (PMVE-MA). Such interpolymer-networked systems were extensively used for biomedical and desalination applications but they were not examined for their potential use as membranes or separators for batteries.
——mdpi.com
- A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings
This review presents the past and current efforts with a brief description on the featured properties of hydrogel membranes fabricated from biopolymers and synthetic ones for wound dressing applications. Many endeavors have been exerted during past ten years for developing new artificial polymeric membranes, which fulfill the demanded conditions for the treatment of skin wounds.
——
- Physicomechanical and antimicrobial characteristics of hydrogel based on poly(vinyl alcohol): Performance improvement via inclusion of chitosan-modified nanoclay
The effect of a chitosan-modified nanoclay (CMNC) on the physical, mechanical, and antimicrobial properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) hydrogels prepared by the electron beam irradiation method is reported in comparison with pristine nanoclay (PNC). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results confirm that the chitosan modification process of nanoclay led to an enhancement in the clay gal- lery spacing.
——
- PVA HYDROGEL
PVA HYDROGEL
——12, United States Patent Muratoglu et al.
- Rapid synthesis of high strength cellulose–poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) biocompatible composite films via microwave crosslinking
The present study describes microwave (MW)-assisted rapid synthesis of biocompatible poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) compos- ite films that demonstrate synergy between reinforcement and crosslinking. Bacterial cellulose (5% w/w) nanowhiskers (reinforcement) and tartaric acid 35% (w/w) (crosslinker) are incorporated in PVA to prepare crosslinked cellulose–PVA composite films.
——
- PVA hydrogel properties for biomedical application
PVA has been proposed as a promising biomaterial suitable for tissue mimicking, vascular cell culturing and vascular implanting. In this research, a kind of transparent PVA hydrogel has been investigated in order to mimic the creatural soft tissue deformation during mini- invasive surgery with needle intervention, such as brachytherapy. Three kinds of samples with the same composition of 3 g PVA, 17 g de-ionized water, 80 g dimethyl-sulfoxide but different freeze/thaw cycles have been prepare
——Shan Jiang∗, Sha Liu, Wenhao Feng
- Investigation of new modification strategies for PVA membranes to improve their dehydration properties by pervaporation
Novel supported membranes based on polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) were developed using two strategies: first, by the modification of the PVA network, via so-called bulk modification, with the formation of the selec- tive layer accomplished through the introduction of fullerenol and/or poly(allylamine hydrochloride), and second, by the functionalization of the surface with successive depositions of multilayered films of polyelectrolytes, such as poly(allylamine hydrochloride) and poly(sodium 4-styrenesu
——Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied
PVA Tube
- Properties and Applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol
The aim of this review was to analyze/investigate the synthesis, properties, and applications of polyvinyl alcohol–halloysite nanotubes (PVA–HNT), and their nanocomposites. Different polymers with versatile properties are attractive because of their introduction and potential uses in many fields.
——NCBI
PVA Ophthalmic Drops
- PVA Tears Eyedrops
PVA TEARS eye drops soothe and lubricate dry eye(s) and provide greater comfort and longer wearing time of hard contact lenses.
——Sibikon R&D
- A Simple PVA Tears Eyedrops Introduction
This is only a copy of simple PVA eyedrops from a AU manufacturer. Just that the reader know how this PVA eyedrop be applied.
——Sibikon R&D
Scientific Literature
- Factors Affecting Wound Healing
Wound healing, as a normal biological process in the human body, is achieved through four precisely and highly programmed phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. For a wound to heal successfully, all four phases must occur in the proper sequence and time frame. Many factors can interfere with one or more phases of this process, thus causing improper or impaired wound healing. This article reviews the recent literature on the most significant factors that affect cutaneous
——NCBI
- Biomaterials of PVA and PVP in medical and pharmaceutical applications: Perspectives and challenges
Keywords:Poly(vinyl alcohol) Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) Biomaterial Tissue engineering Drug delivery Wound dressing.
——Mirela Teodorescu, Maria Bercea, Simona Morariu